What is NLP Pipeline?
The NLP pipeline can be thought of as a funnel, with the raw text entering at the top and the final predictions emerging at the bottom. Each step in the pipeline helps to narrow the focus and extract more meaningful information from the text.

There are three main steps involved when you pass some text to a pipeline:
The text is preprocessed into a format the model can understand.
The preprocessed inputs are passed to the model.
The predictions of the model are post-processed, so you can make sense of them.
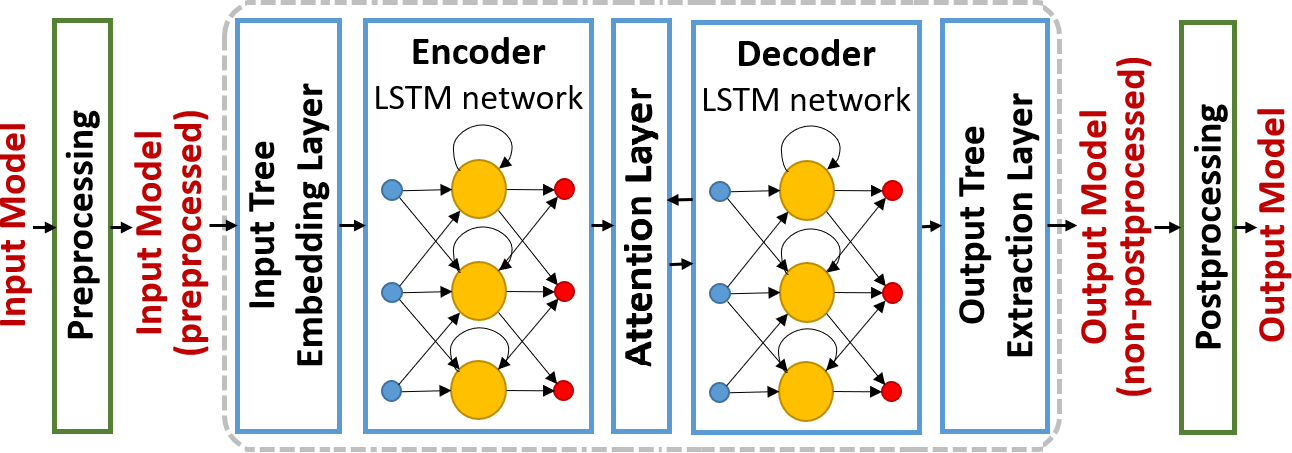
(will be covering each step in detail later 😊)
The key task performed by NLP Pipeline (Complete list)
Sentiment-analysis
Zero-shot classification
fill-mask
question-answering
summarization
text-generation
translation
Will be covering codes for the above-mentioned task using hugging face.
Steps to use pipeline from Hugging Face
Step 1: Install the transformer library
!pip install transformers
Step 2: Use the pipeline from the transformer library
from transformers import pipeline
Step 3: Use the task from the pipeline
classifier = pipeline("sentiment-analysis")
or with a mentioned model (eg: specific to the financial market)
from transformers import pipeline
classifier = pipeline(model="ProsusAI/finbert")
classifier("stocks dropped 42% while Samsung rallied")
# [{'label': 'negative', 'score': 0.9670934081077576}]
Step 4: Use the selected task pipeline for the task output generation for the given input.
classifier("This is the worst possible product. Nothing works in this.")
# [{'label': 'NEGATIVE', 'score': 0.9998025298118591}]
# model : distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-sst-2-english
Zero-shot classification
Zero-shot learning (ZSL) in NLP is a machine learning technique that allows a model to classify text from previously unseen classes, without receiving any specific training for those classes. This is done by leveraging the model's understanding of the semantic relationships between words and concepts.
There are two main approaches to ZSL in NLP:
Attributes-based ZSL: This approach uses a set of attributes to describe the unseen classes. The model is then trained to map these attributes to class labels.
Semantic-based ZSL: This approach uses a knowledge base to represent the semantic relationships between words and concepts. The model is then trained to use this knowledge base to make predictions about unseen classes.
from transformers import pipeline
classifier = pipeline("zero-shot-classification")
classifier(
"Airpods are the best",
candidate_labels=["education", "politics", "technology", "business"],
)
# Output
{'sequence': 'Airpods are the best',
'labels': ['technology', 'business', 'education', 'politics'],
'scores': [0.9303504228591919,
0.048402491956949234,
0.012988047674298286,
0.008259052410721779]}
Text generation
For the provided prompt, the model will auto-complete it by generating the remaining text. This is similar to the predictive text feature that is found on phones or the gmail next words suggestion.
from transformers import pipeline
generator = pipeline("text-generation")
generator("Apple is one of the biggest")
Output
[{'generated_text': 'Apple is one of the biggest players in the PC gaming industry. The company recently signed licensing agreements with some very notable companies including AMD, NVIDIA, and Electronic Arts. PC gaming has been a huge success across the board, with the release of more copies'}]
Mask filling
the task is to fill in the blanks in a given sentence.
from transformers import pipeline
unmasker = pipeline("fill-mask")
unmasker("Apple is <mask> for the tech industry.", top_k=2) #top_k is to limit results, will fetch top_k results only
[{'score': 0.08616828173398972,
'token': 2149,
'token_str': ' responsible',
'sequence': 'Apple is responsible for the tech industry.'},
{'score': 0.037314582616090775,
'token': 12115,
'token_str': ' bullish',
'sequence': 'Apple is bullish for the tech industry.'}]
Question answering
from transformers import pipeline
question_answerer = pipeline("question-answering")
question_answerer(
question="What is aim of ChatGPT",
context="ChatGPT is an advanced language model designed to assist users with a wide range of inquiries. Powered by the GPT-3.5 architecture, it leverages extensive training data to provide accurate and coherent responses. With its natural language processing capabilities, ChatGPT aims to enhance communication and offer valuable information, making it a valuable tool in various domains.",
)
{'score': 0.32861292362213135,
'start': 277,
'end': 332,
'answer': 'to enhance communication and offer valuable information'}
Summarization
from transformers import pipeline
summarizer = pipeline("summarization")
summarizer(
"""
ChatGPT is an impressive feat of artificial intelligence, revolutionizing the way we interact with computer systems. Developed by OpenAI, it is built upon the powerful GPT-3.5 architecture, which enables it to generate human-like responses to user queries.
With a vast amount of training data, ChatGPT has been exposed to a diverse range of topics, making it well-equipped to provide accurate and insightful information. Whether you need assistance with general knowledge, technical inquiries, or even creative writing prompts, ChatGPT can offer valuable guidance.
The natural language processing capabilities of ChatGPT allow it to understand and respond to a wide array of linguistic nuances. It can decipher the context of a question and generate coherent and contextually appropriate answers. Moreover, ChatGPT can engage in conversational dialogues, adapting its responses to maintain a seamless interaction.
While ChatGPT excels at providing information, it is important to note that it operates within the limits of its training data. It may occasionally produce incorrect or incomplete answers, and it lacks the ability to verify the accuracy of the information it provides. Users should exercise critical thinking and verify facts independently when necessary.
OpenAI has implemented measures to ensure the responsible use of ChatGPT, such as its knowledge cutoff date and the ability to flag and address biased or inappropriate content. These efforts aim to create a safe and reliable environment for users.
As an AI language model, ChatGPT is continuously evolving. OpenAI actively seeks user feedback to improve its performance and address any limitations. The goal is to refine and enhance ChatGPT's capabilities, making it an even more valuable tool for individuals and businesses alike.
Overall, ChatGPT represents a significant advancement in conversational AI, bridging the gap between humans and machines. It has the potential to transform various industries and revolutionize the way we interact with technology, paving the way for a future where intelligent virtual assistants are an integral part of our daily lives.
"""
)
Output
[{'summary_text': ' ChatGPT is an impressive feat of artificial intelligence, revolutionizing the way we interact with computer systems . It is built upon the powerful GPT-3.5 architecture, which enables it to generate human-like responses to user queries . It can decipher the context of a question and generate coherent and contextually appropriate answers .'}]
Translation
# Install sentencepiece
!pip install transformers[sentencepiece]
# restart the kernel
Looking in indexes: https://pypi.org/simple, https://us-python.pkg.dev/colab-wheels/public/simple/
Requirement already satisfied: transformers[sentencepiece] in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (4.30.2)
Requirement already satisfied: filelock in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from transformers[sentencepiece]) (3.12.0)
Requirement already satisfied: huggingface-hub<1.0,>=0.14.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from transformers[sentencepiece]) (0.15.1)
Requirement already satisfied: numpy>=1.17 in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from transformers[sentencepiece]) (1.22.4)
Requirement already satisfied: packaging>=20.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from transformers[sentencepiece]) (23.1)
Requirement already satisfied: pyyaml>=5.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from transformers[sentencepiece]) (6.0)
Requirement already satisfied: regex!=2019.12.17 in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from transformers[sentencepiece]) (2022.10.31)
Requirement already satisfied: requests in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from transformers[sentencepiece]) (2.27.1)
Requirement already satisfied: tokenizers!=0.11.3,<0.14,>=0.11.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from transformers[sentencepiece]) (0.13.3)
Requirement already satisfied: safetensors>=0.3.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from transformers[sentencepiece]) (0.3.1)
Requirement already satisfied: tqdm>=4.27 in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from transformers[sentencepiece]) (4.65.0)
Requirement already satisfied: sentencepiece!=0.1.92,>=0.1.91 in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from transformers[sentencepiece]) (0.1.99)
Requirement already satisfied: protobuf<=3.20.3 in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from transformers[sentencepiece]) (3.20.3)
Requirement already satisfied: fsspec in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from huggingface-hub<1.0,>=0.14.1->transformers[sentencepiece]) (2023.4.0)
Requirement already satisfied: typing-extensions>=3.7.4.3 in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from huggingface-hub<1.0,>=0.14.1->transformers[sentencepiece]) (4.5.0)
Requirement already satisfied: urllib3<1.27,>=1.21.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from requests->transformers[sentencepiece]) (1.26.15)
Requirement already satisfied: certifi>=2017.4.17 in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from requests->transformers[sentencepiece]) (2022.12.7)
Requirement already satisfied: charset-normalizer~=2.0.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from requests->transformers[sentencepiece]) (2.0.12)
Requirement already satisfied: idna<4,>=2.5 in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (from requests->transformers[sentencepiece]) (3.4)
Tranlation Model list : huggingface.co/models?pipeline_tag=translat..
from transformers import pipeline
translates = pipeline("translation",model="Helsinki-NLP/opus-mt-en-hi")
translates("Apple has an ecosystem of devices.")
[{'translation_text': 'एप्पल उपकरणों का एक पर्यावरण है.'}]
# model="Helsinki-NLP/opus-mt-en-hi" translate en(english) to hi(hindi)
# model="Helsinki-NLP/opus-mt-hi-en" translate hi(hindi) to en(english)
translates = pipeline("translation",model="Helsinki-NLP/opus-mt-hi-en")
translates("एप्पल उपकरणों का एक पर्यावरण है.")
[{'translation_text': 'The Appall devices have an environment.'}]
